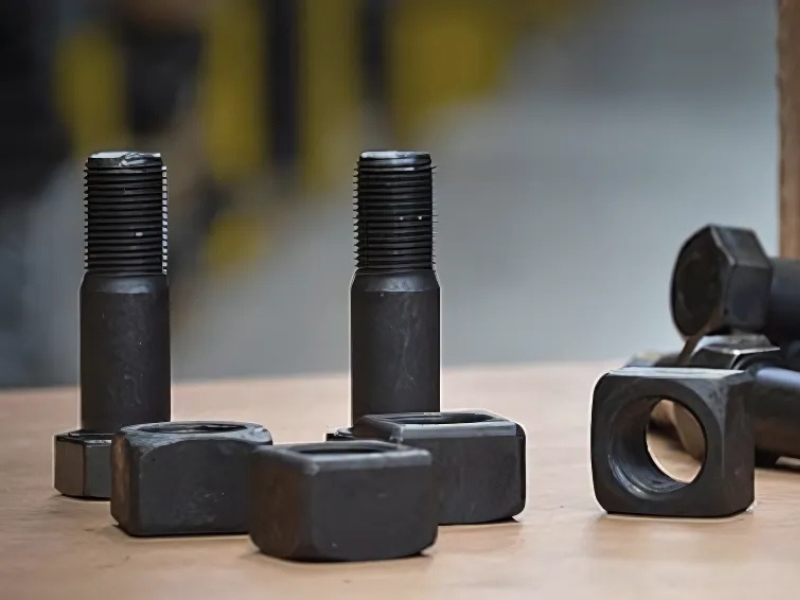

Coastal environments pose unique challenges for construction and heavy‑equipment hardware. Salt‑laden air, high humidity, and frequent temperature swings accelerate corrosion—undermining structural integrity and increasing maintenance costs. That’s why selecting the right corrosion‑resistant bolts, especially for heavy machinery like excavators working near the shoreline, is critical. In this post, we shine a spotlight on Excavator Bolts—designed to withstand harsh coastal conditions without compromising strength or performance.
Coastal areas accelerate oxidation, especially of steel and iron components. Saltwater aerosols penetrate protective coatings, instigating pitting, rust, and galvanic corrosion. Over time, standard bolts degrade—leading to loose joints, failures, and expensive replacements. Coastal‑grade hardware must resist these environmental stressors without sacrificing load‑bearing capacity.
Excavator Bolts are heavy‑duty fasteners engineered for earth‑moving equipment—like excavators, backhoes, and loaders. These bolts typically feature:
High‑tensile alloy steel shafts rated to resist shear and tensile loads under extreme vibration and force.
Oversized hex heads or flange heads for improved torque control and resistance to loosening.
Special coatings or material blends such as stainless steel, zinc‑nickel plating, or weathering steel (COR‑TEN) to enhance corrosion resistance.
What sets Excavator Bolts apart in coastal projects is the thoughtful integration of mechanical strength with durable corrosion protection.
Let’s delve into the corrosion‑fighting features typically embedded in these bolts:
316 Stainless Steel: Rich in chromium, nickel, and molybdenum for exceptional resistance to chloride-induced corrosion.
High‑Performance Alloy Steels: Custom alloys often treated for coastal durability.
Zinc‑Nickel (Zn‑Ni) coatings provide superior galvanic protection even when scratched—ideal under salt spray.
Hot‑dip Galvanizing yields thick, robust protection—but may require extra finishing for tight tolerances.
Duplex Coatings (e.g., zinc plus passivated topcoat) can push performance even further.
Anti‑seize lubricants embedded in threads protect against galling and corrosion, ensuring bolts remain serviceable even after extended exposure.
PTFE or wax-based sealants repel moisture ingress and reduce galling in dissimilar metal contacts.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| High Load Strength | Designed for heavy-duty mining-grade operations—can handle dynamic excavation forces. |
| Intelligent Corrosion Design | Built from materials and finishes tailored for marine environments. |
| Longevity & Maintenance Savings | Reduced failures, extended service life, lower inspection and replacement costs. |
| Ease of Installation & Security | Oversized heads and lubricated threads ensure secure torque and easier servicing. |
Inspect Before Use
Ensure the bolts show no scoring, cracks, or coating irregularities—those compromise corrosion protection.
Apply Corrosion‑Protective Lubricant
Even coated bolts benefit from a thin layer of marine-grade anti‑seize lubricant to further seal the threads and prevent galling.
Proper Torque Control
Over‑ or under‑torque can degrade both mechanical and protective integrity. Use calibrated torque tools and follow manufacturer specs.
Routine Inspection
Schedule bolt inspections after high‑exposure events—like storms. Look for coating damage, surface rust, or loosening.
Replace Damaged Bolts Promptly
Any visible corrosion or coating failure demands immediate bolt replacement to avoid structural compromise.
Imagine a coastal dock reinforced using heavy-duty steel beams anchored with Excavator Bolts. These bolts endure tidal spray, storm surges, and constant vibration from equipment operations. Installed with Zn‑Ni plated threads, stainless alloy shafts, and sealed lubricant layers, they resist marine corrosion while sustaining high loads. Years later, inspections reveal intact coatings and stable torque—no signs of rust or degradation. The result? Minimal maintenance, fewer downtime occurrences, and robust structure integrity.
To optimize this blog post for search engines:
Title & Heading Usage
Title: Corrosion‑Resistant Excavator Bolts for Coastal Projects
Subheadings: “Why Excavator Bolts Are Perfect for Coastal Projects” etc.
Keyword Density
Use “Excavator Bolts” strategically—intro, headings, body—without over‑stuffing.
Latent Semantic Variants
Include related phrases like “marine‑grade fasteners,” “coastal hardware,” “salt‑resistant bolts,” and “heavy‑duty corrosion‑resistant bolts.”
Meta Description (suggestion)
“Discover why Excavator Bolts stand up to salt‑air, vibration, and heavy loads—perfect corrosion‑resistant fasteners for coastal construction.”
For coastal projects, standard hardware just won’t cut it. Environmental exposure demands more: durability, corrosion resistance, and strength. Excavator Bolts deliver all three—engineered for the rigors of heavy machinery and the corrosive threats of coastlines. Use the right grade, maintain them carefully, and inspect them regularly—and these bolts will anchor your coastal construction for years to come.









Excavator Rock Bucket | Excavator Skeleton Bucket | Excavator Trapezoidal Bucket | Excavator Soil Bucket | Excavator Loader Bucket | Excavator Single-Shank Ripper | Excavator Triple-Shank Ripper | Excavator Track Link Assembly | Excavator Tooth Points | Excavator JCB Teeth & Side Cutter | Excavator Idler | Excavator Sprocket | Excavator Lower Roller | Excavator Undercarriage | Excavator Track Group | Excavator Bolts | Excavator Rock Bucket in Chennai | Excavator Skeleton Bucket in Chennai | Excavator Trapezoidal Bucket in Chennai | Excavator Soil Bucket in Chennai | Excavator Loader Bucket in Chennai | Excavator Single-Shank Ripper in Chennai | Excavator Triple-Shank Ripper in Chennai | Excavator Track Link Assembly in Chennai | Excavator Tooth Points in Chennai | Excavator JCB Teeth & Side Cutter in Chennai | Excavator Idler in Chennai | Excavator Sprocket in Chennai | Excavator Lower Roller in Chennai | Excavator Undercarriage in Chennai | Excavator Track Group in Chennai | Excavator Bolts in Chennai | Excavator Rock Bucket in India | Excavator Skeleton Bucket in India | Excavator Trapezoidal Bucket in India | Excavator Soil Bucket in India | Excavator Loader Bucket in India | Excavator Single-Shank Ripper in India | Excavator Triple-Shank Ripper in India | Excavator Track Link Assembly in India | Excavator Tooth Points in India | Excavator JCB Teeth & Side Cutter in India | Excavator Idler in India | Excavator Sprocket in India | Excavator Lower Roller in India | Excavator Undercarriage in India | Excavator Track Group in India | Excavator Bolts in India
TEAM. All Rights Reserved. Developed by Pixel Tech.